Computer hardware refers to the physical parts of a computer system, whereas software refers to the machine-readable instructions that tell a computer’s processor what to do.
In Lecture 1 and 2 of Intro CS, we talked about the Von Neumann Architecture of a stored-program computer. In 1945, mathematician and physicist Von Neumann first wrote about the logical design of a stored-program computer in this publication, entitled: First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC.
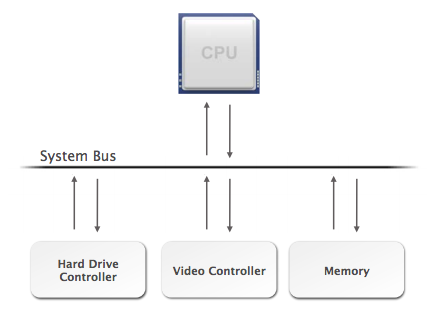
According to Von Neumann, the basic components of a computer include a processing unit, with an ariithmetic logic unit and processor registers, a control unit with an instruction register and program counter, a memory bank to store data and instructions, external memory/mass storage, and input/output mechanisms.
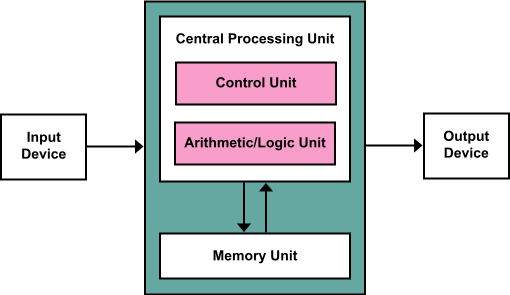
Here are what these components look like in our common personal computer (PC) hardware setup:
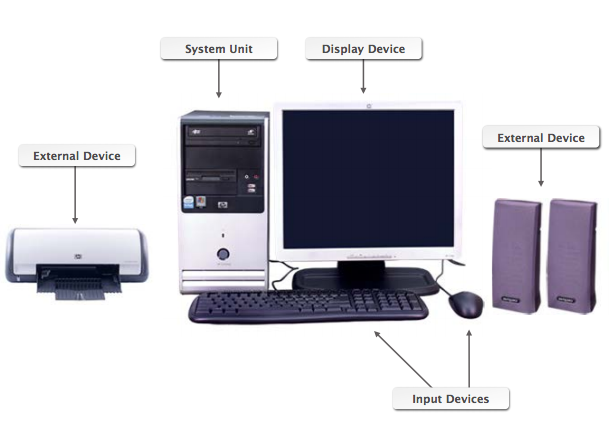
Common Computer Components
We have a computer case, which houses most of the hardware components. There are also input devices such as a mouse and a keyboard, or a touchpad/touchscreen on laptops and tablets. Webcams, microphones, joysticks, and image scanners are also examples of input devices. We also have output devices such as printers, speakers, or Braille embossers. In desktop computers, we also have a monitor screen display device, which is packed into the computer case in smaller laptops, tablets, and mobile devices.
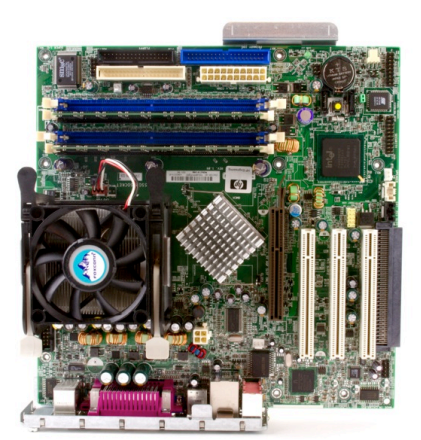
==================== 1. Motherboard ====================
The motherboard is the main component of computer, with integrated circuitry that connects all other computer parts, including the CPU, the RAM, the disk drives(CD, DVD, hard disk, or any others) and expansion slots.
==================== 2. Central Processing Unit (CPU) ====================
CPU
The CPU is the “brain” of the computer, which performs most computer calculations. A chipset mediates communication between the CPU and other system components.
==================== 3. Memory Bank ====================

Memory
There are two types of memory:
1. Random Access Memory (RAM) stores the code and data that is actively accessed by the CPU. It is volatile memory that can get lost when you shut off computer power without saving.
2. Read-Only Memory (ROM) contains non-volatile memory and firmware, which controls the basic operations of your computer, and the System BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), which tells the computer what to do when it boot up (bootstrapping).
Firmware
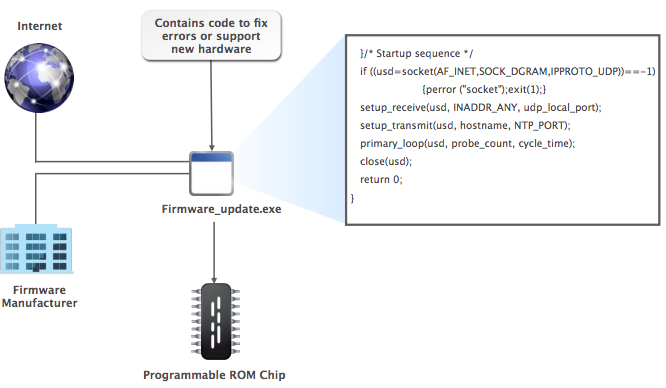
Firmware
System BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)
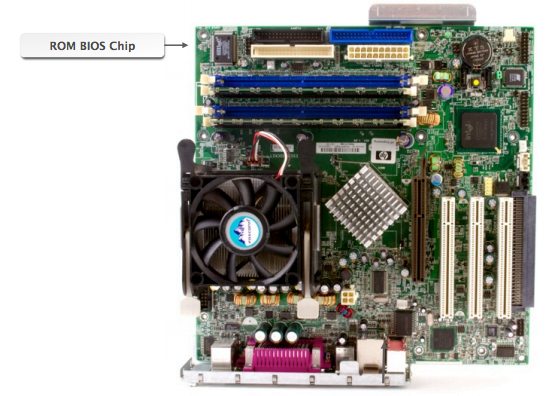
System BIOS
==================== 4. System Bus ====================
The System Bus is a wire structure that connects the CPU to various internal components, and contains slots for adapter cards and expansion cards such as graphics, video, and sound cards.
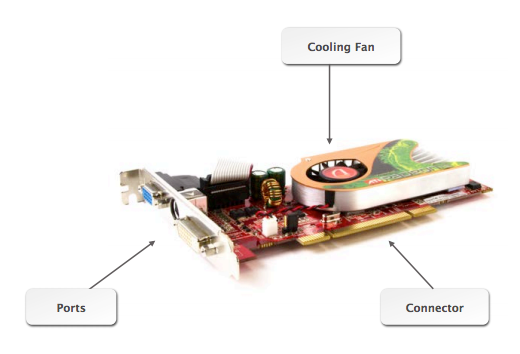
Expansion Cards add functionality to a computer system. It’s a printed circuit board that can be inserted into the expansion bus in the motherboard or backpane.
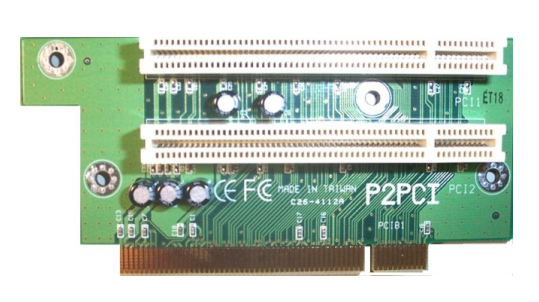
Riser Cards allow for adding more slots to the system bus. They are usually used in rack mounts and servers, rather than in smaller personal computers.
==================== 5. Storage Devices ====================
Storage devices retain digital data, including fixed media and removable media. Fixed media include hard disk drives and solid-state drives which are faster and more power efficient. Removable media are used to transfer data between computers, such as USB flash drives, or optical discs (CD/DVD, and remember those old floppy disks? Yeah those…)
==================== 6. Power Supply Unit (PSU) ====================
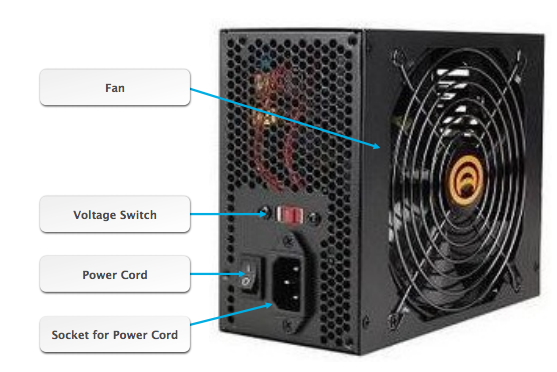
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The PSU consists of a power switch, power cord, fans, and a voltage switch
(120-volts in the U.S. and 220-volts in some other countries)
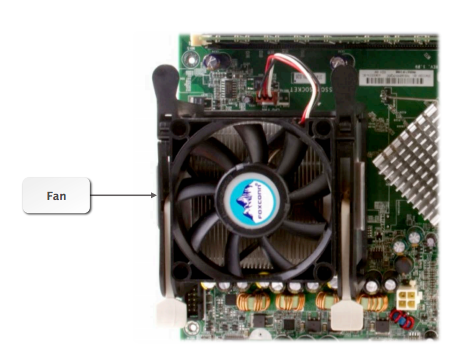
Cooling Systems: fans are placed next to various parts to the computer, including the hard disk drives and some expansion cards, to keep cool.
//======================================== //
Those are the main hardware components of a common personal computer!
When you turn on your computer, it runs a routine on-board diagnostic called a POST (Power On Self-Test) to check that all the components are working.

Power On Self-Test (POST)